Ionix – Parkwalk closes follow-on investment
We are pleased to announce that the Parkwalk Opportunities EIS Fund has participated in a follow-on financing round into Ionix Advanced Technologies, a Leeds University Spin-out that has developed extreme temperature piezo technology for use in the protection of high value industrial assets. Parkwalk invested alongside existing investor IP Group plc.
The market for piezo technologies –harnessing certain material’s capacity to transform pressure into power or, alternatively, power into pressure – is already widespread and growing. The piezoelectric market is well established but applications are limited by the properties of the materials currently in use.
8power – Joins the LoRa Alliance™
8power is pleased to announce membership of the LoRa Alliance™, a global industry group to promote the development and deployment of the LoRaWAN™ Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) open standard. The Alliance represents many of the leading players in the wireless Internet of Things community, including global enterprises, major network operators, service providers, device developers and end customers.
8power will shortly be launching its first LoRaWAN™ compliant devices for asset tracking, machine condition, and critical infrastructure monitoring. The company’s products are designed to solve the problem of powering wireless sensor devices in the field without the need for mains power supply or regular battery charge/replacement. 8power’s expertise in low-power system design coupled with its patented energy harvesting technology makes these products an ideal fit for leading wireless IoT applications.
Antony Rix, CEO of 8power, said: “Joining the LoRa Alliance™ is a key step for 8power, allowing us to sell devices based on this LPWAN technology to meet some of our customers’ most challenging requirements. We look forward to working with the LoRaWAN™ community and other leading LPWANs in the coming months as we extend our device portfolio.”
8power plans to support all major LPWAN standards and will be launching other versions later this year to support LTE CAT-M and NB-IoT, other cellular standards, and SIGFOX.
The company will be demonstrating its first products at the following trade shows.
- Mobile World Congress, Barcelona, Spain Feb 27th – March 2nd 2017
- ConExpo – Con/Agg, Las Vegas, Nevada, US March 7th – 11th 2017
- IDTechEx, Berlin, Germany May 10th – 11th 2017
Please contact us at expo@8power.com to arrange a demonstration of our end to end solutions.
ENDS
About 8power
8power is a new start-up company commercialising novel vibration energy harvesting (VEH) technology developed by researchers from the University of Cambridge. The target markets for the technology are self-powered wireless & IoT devices for sensing and measurement in industrial applications.
VEH enables power to be generated from a variety of vibration sources including motors, moving vehicles, or traffic-induced movement in structures such as bridges. The patented technology delivers 10 times higher electrical power than existing VEH systems by employing the principle of parametric resonance. This exciting discovery was pioneered by leading academics at the Centre for Smart Infrastructure and Construction at the University of Cambridge.
For more information
Please contact 8power on +44 1223 781610 or through www.8power.com
Cambridge Touch Technologies – follow-on investment
We have recently made a follow-on investment in Cambridge Touch Technologies for the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund IV, the Parkwalk UK Tech Fund VII and the Parkwalk Opportunities Fund in a series ‘A’ financing round.
Cambridge Touch Technologies (CTT), a University of Cambridge start-up poised to make 3D touch technology a standard feature on smart devices, has received seed investment by Cambridge Enterprise, the commercialisation arm of the University.
The details of the investment have not been disclosed.
CTT’s next generation 3D touch technology enables mobile devices to sense both the location and force of multi-touch inputs. CTT’s technology improves on the first generation of 3D technologies recently introduced to mass markets, which allow users to press a phone’s touch screen – exerting force – to access useful new interactions such as ‘peek and pop’ and ‘left-click’ functionality. Unlike this first generation technology, CTT has developed a sensitive multi-touch technology that can sense ‘multi finger’ force, is more scalable and cost-effective without any decrease in battery life. As a result, force-sensing technology, which currently offers limited functionality and is only available in smartphone-sized devices, can potentially be expanded and deployed on any touch screen – from smartphones to tablets to those in automobiles and beyond.
Since 2011, CTT has been developing its leading and patent pending analogue circuitry and digital algorithms, which leverage the existing manufacturing processes and standard architectures of conventional projected capacitive touch. CTT’s technology will lead to more immersive apps, better gaming experiences and higher everyday user satisfaction and productivity.
“We’ve added in improved performance and taken out the complexity,” said Corbin Church, CEO of CTT. “The technology can now be adapted in more formats and deployed in a larger part of the market at a lower cost.”
Dr Arokia Nathan, CTO and co-founder of CTT, and Professor of Photonic Systems and Displays at the University of Cambridge’s Department of Engineering, said “the elegance of this new 3D touch technology lies in the simplicity of signal acquisition, signal processing and digital noise reduction, and it really opens the door for 3D touch to a new generation of applications.”
3D touch-enabled devices are expected to grow to more than 900 million units annually in 2020, according to IHS Technology.
Proxisense – Parkwalk closes University of Oxford Innovation Fund III investment
We are delighted to announce that the University of Oxford Innovation Fund III has invested in Proxisense, an Oxford University spinout supplying specialised proximity sensors and systems to measure contamination in critical fluid systems. These products have been developed for use is for extreme and inaccessible environments.
The proximity sensor technology utilises an eddy current sensor and enables the very accurate measurement of the position of components in real time. For example, the position of the tips of turbine blades and the monitoring of blade vibration whilst the systems are in use. This enables Proxisense to provide comprehensive health-monitoring technology which allows the user to detect degrading performance and the possible onset of component failure
PervasID – University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund IV investment
We are delighted to announce that the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund IV, managed by Parkwalk, has invested in PervasID, a spin-out from the Department of Engineering.
The company has developed a long-range passive Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tracking technology which substantially outperforms current passive RFID technologies. Crucially, it allows low-cost commodity RFID tags to be utilised in long range applications achieving accuracy until now only achievable using more expensive active RFID.
8Power – University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III investment
We have recently made an investment in 8Power for the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III in a financing round.
8power Limited, a new company spun out of the University of Cambridge to develop and commercialise novel technology for sensing and measurement in industrial applications, has received initial funding of approximately £700,000 from IP Group plc (LSE: IPO), the University of Cambridge and the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III, managed by Parkwalk Advisors.
The University of Cambridge is a world leader in the science and technology of sensing, and is pioneering the research of new sensor technologies applied to condition monitoring of built infrastructure and machinery through the Cambridge Centre for Smart Infrastructure and Construction and a number of other research groups. A system that can monitor its own condition automatically can be cheaper to build, for example by using less material, or easier to maintain, for example by scheduling servicing when needed rather than on a regular timetable.
While techniques to connect and monitor large numbers of devices (often termed the Internet of Things, IoT) are starting to mature, 8power’s technologies bring unique benefits, as they provide ways to power sensors from ambient vibration, and permit the creation of new types of sensors with dramatically lower power consumption than before. The company’s products and services are applicable to a number of markets, including automotive and transportation, civil engineering, industrial equipment, and utility infrastructure.
The core technologies that the company has licensed from Cambridge Enterprise, the commercialisation arm of the University of Cambridge, were developed by a team led by Dr Ashwin Seshia at the University’s Department of Engineering. Dr Seshia, who recently co-founded Silicon Microgravity, will head the company’s advisory board, joined by three other academic founders from this team, Dr Yu Jia, Lecturer at the University of Chester, Dr Jize Yan, Associate Professor at the University of Southampton, and Prof. Kenichi Soga, Chancellor’s Professor at the University of California, Berkeley. The company will shortly announce that it has appointed a leading expert in wireless communications and IoT as CEO.
Dr Ashwin Seshia, co-founder of 8power, said “8power combines a number of unique world-leading technologies in energy harvesting and microelectromechanical systems to provide the basis for new energy autonomous sensor systems that can address a range of application scenarios. We are excited by the opportunity to accelerate technology translation via 8power and look forward to working together with our partners to further develop and deploy these technologies as widely as possible.”
Parkwalk portfolio company CCMOSS – acquired by ams AG to become world leader in gas and infrared sensing
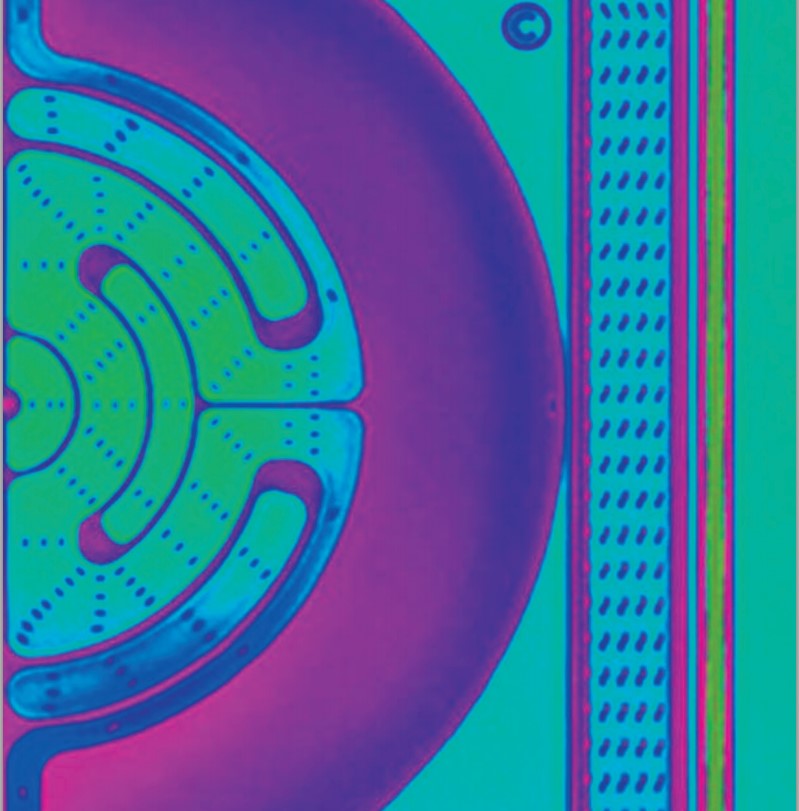
ams AG (SIX: AMS), a leading worldwide manufacturer of high performance sensor and analog solutions, has acquired 100% of the shares in Cambridge CMOS Sensors Ltd (CCS), the technology leader in micro hotplate structures for gas sensing and infrared applications, in an all-cash transaction.
Founded in 2008 as a spin-off from Cambridge University, with the start of technology development dating back to 1994 in collaboration with the University of Warwick, CCS has built an outstanding expertise in micro hotplate design and manufacturing for gas and infrared sensing over more than 20 years. Parkwalk and Cambridge Enterprise, the commercialisation arm of the University of Cambridge, have supported CCS throughout its development.
CCS’ micro hotplates are MEMS structures that are used in gas sensors for volume applications in the automotive, industrial, medical, and consumer markets. The company’s deep expertise in this area is highly synergetic with ams’ technology leadership in MOX gas sensing materials to detect gases like CO, NOx, and VOCs. CCS manufactures these MEMS structures on CMOS wafers allowing the creation of complete monolithically integrated CMOS sensor ICs. This makes CCS’ solutions highly cost-efficient, besides offering other significant advantages over competing technologies like low power consumption, small footprint and the ability to integrate additional sensor modalities like relative humidity, temperature, and pressure.
“The addition of CCS makes ams the clear leader in gas and infrared sensor technology worldwide, and completes ams’ portfolio of products and technologies for the environmental sensor market.”
Alexander Everke
In addition, CCS commands an industry-leading portfolio of IR technology comprising high performance IR radiation sources and detectors for sensor applications. Highly complementary to ams’ spectral sensing strategy for next generation optical sensor technologies, CCS’ IR sensing is based on the same monolithic CMOS structures as for gas sensing, enabling miniaturised implementations and efficient integration with other on-chip functions. Applications include CO2 gas sensing and human presence detection and will extend into spectroscopic identification of organic materials.
CCS’ corporate headquarters are located in Cambridge, UK, and the company has 33 employees. The Cambridge region has become a centre of innovation for sensor technologies globally so ams values the ability to gain direct access to this attractive ecosystem going forward.
The parties to the transaction have agreed to keep the consideration confidential. ams plans to fully integrate CCS’ activities into its existing environmental sensor business, which has development locations in Eindhoven, the Netherlands, and Reutlingen, Germany.
Cambridge Touch Technologies – University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III investment
We have recently made an investment in Cambridge Touch Technologies for the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III in a seed financing round.
Cambridge Touch Technologies (CTT), a University of Cambridge start-up poised to make 3D touch technology a standard feature on smart devices, has received seed investment by Cambridge Enterprise, the commercialisation arm of the University.
The details of the investment have not been disclosed.
CTT’s next generation 3D touch technology enables mobile devices to sense both the location and force of multi-touch inputs. CTT’s technology improves on the first generation of 3D technologies recently introduced to mass markets, which allow users to press a phone’s touch screen – exerting force – to access useful new interactions such as ‘peek and pop’ and ‘left-click’ functionality. Unlike this first generation technology, CTT has developed a sensitive multi-touch technology that can sense ‘multi finger’ force, is more scalable and cost-effective without any decrease in battery life. As a result, force-sensing technology, which currently offers limited functionality and is only available in smartphone-sized devices, can potentially be expanded and deployed on any touch screen – from smartphones to tablets to those in automobiles and beyond.
Since 2011, CTT has been developing its leading and patent pending analogue circuitry and digital algorithms, which leverage the existing manufacturing processes and standard architectures of conventional projected capacitive touch. CTT’s technology will lead to more immersive apps, better gaming experiences and higher everyday user satisfaction and productivity.
“We’ve added in improved performance and taken out the complexity,” said Corbin Church, CEO of CTT. “The technology can now be adapted in more formats and deployed in a larger part of the market at a lower cost.”
Dr Arokia Nathan, CTO and co-founder of CTT, and Professor of Photonic Systems and Displays at the University of Cambridge’s Department of Engineering, said “the elegance of this new 3D touch technology lies in the simplicity of signal acquisition, signal processing and digital noise reduction, and it really opens the door for 3D touch to a new generation of applications.”
3D touch-enabled devices are expected to grow to more than 900 million units annually in 2020, according to IHS Technology.
RoadMap – University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III investment
We have recently made an investment in RoadMap for the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III in a Series ‘A’ financing.
RoadMap is founded on four patents licensed from the Cambridge Centre for Advanced Photonics and Electronics (CAPE) in the area of silicon wavelength switch technology.
Network operators are facing the triple challenge of increasing capacity to fulfil exploding internet data needs, managing unrelenting downward pressure on Opex and Capex costs, and supporting variable and fast evolving service features and demand patterns that put a premium on network configuration flexibility. This leads to a requirement for very flexible optical switching that can operate at the wavelength level. Conventional switch architectures no longer meet this need as they cannot accommodate next generation 400 Gbps data rates.
The telecommunication industry is also migrating towards ‘flexgrid’ architectures where the capacity of each channel is moderated to satisfy fluctuating demands. Spare capacity freed up by this can accommodate additional or rerouted traffic flexibly and dynamically by matching channel bandwidths to each signal’s required data rate. This advance relies heavily on software based approaches and these have the added benefit of future proofing networks as the software defined network (SDN) can be remotely modified to accommodate changing demand and new service types, protocols or standards. This is all accomplished without hardware network upgrades or physical interventions, thus reducing costs. The market is expanding with new customers (such as Google and Amazon) joining the existing set of Telco’s and carriers.
Flex-grid networking places severe demands on the underlying hardware, especially optical switches within the network known as a Reconfigurable Optical Add/Drop Multiplexers (“ROADMs”) which must be competitive and have good manufacturability whilst being able to accommodate the flexibility and programmable functionality required. Within ROADM the Wavelength Selective Switches (WSS) is the key component. The ROADM market has grown from zero to $5bn since 2002. The market has already chosen RoadMap’s core technology, namely Liquid crystal on silicon (“LCoS”) as the way in which WSS’s will be made as it has several major advantages. It allows nearly all parameters to be programmable and upgraded by software-remotely and efficiently.
Parkwalk closes Navetas investment
We are pleased to announce that the Parkwalk Opportunities Fund has made an investment in Navetas, a University of Oxford spin-out with a core product offer of Loop Energy Saver, a consumer install, online, electricity and gas residential energy monitor with a built in tariff tracker and switching service in partnership with uSwitch to keep users on the best tariff.
Ionix – Parkwalk closes investment
We are pleased to announce that the Parkwalk Opportunities EIS Fund has participated in a financing round into Ionix Advanced Technologies, a Leeds University Spin-out that has developed extreme temperature piezo technology for use in the protection of high value industrial assets. Parkwalk invested alongside existing investor IP Group plc.
The market for piezo technologies –harnessing certain material’s capacity to transform pressure into power or, alternatively, power into pressure – is already widespread and growing. The piezoelectric market is well established but applications are limited by the properties of the materials currently in use.
Ionix Advanced Technologies was spun-out of the University of Leeds In 2011. The company has developed a proprietary device (modifiable to suit different applications), based on its novel piezoceramic material, which enables the protection of high value industrial assets in extreme temperature conditions.
In addition to being one of the very few high activity piezo technologies capable of operating above 250°C, Ionix’s devices are simpler, lower cost and easier to install than the limited alternatives already in use (largely dominated by manual inspection devices).
CCMOSS – Parkwalk closes further funding round
We have recently made an investment in Cambridge CMOS Sensors for the Parkwalk Opportunities EIS Fund and the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund III.. This follows predecessor funds investing in 2012 and 2013.
Cambridge CMOS Sensors is a leading manufacturer of sensor solutions for monitoring air quality, with a wide range of miniature, ultra-low power gas sensors based on metal-oxide technology and infrared sensor components.
Cambridge CMOS Sensors is a spin-out from University of Cambridge and is exploiting innovative patented technology jointly developed in collaboration with the University of Warwick. The company aims to be a technology provider of CMOS MEMS structures such as basic and smart micro-hotplates, semiconductor sensors (gas sensors, mechanical sensors, temperature sensors & flow sensors) and nano-MEMS and nanosensors and a leading manufacturer of mid-infrared emitter.
CMOS MEMS platform technology provides a unique silicon platform for CCMOSS’ Metal Oxide (MOX) gas sensors and enables sensor miniaturisation, significantly lower power consumption and ultra-fast response times.
The Micro-hotplates are suspended in a high reliability membrane and act as heater elements for a metal oxide based sensing material. The material resistance will change due to reactions to selected gases and concentrations at temperatures between 200°C to 400°C. Through enabling very fast cycle times, advanced temperature modulation techniques can be used to ensure maximum sensitivity, stability and gas selectivity and minimise measurement times.
Advanced algorithms support the MOX gas sensors family, for maximum selectivity, drift compensation and for self-calibration, enabling easy and timely integration into a wide range of applications.
RoadMap – University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund II investment
We have recently made an investment in RoadMap for the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund II in a first round of financing of £515k. It is envisioned that a further financing round will be required in 12 months.
RoadMap is founded on four patents licensed from the Cambridge Centre for Advanced Photonics and Electronics (CAPE) in the area of silicon wavelength switch technology.
Network operators are facing the triple challenge of increasing capacity to fulfil exploding internet data needs, managing unrelenting downward pressure on Opex and Capex costs, and supporting variable and fast evolving service features and demand patterns that put a premium on network configuration flexibility. This leads to a requirement for very flexible optical switching that can operate at the wavelength level. Conventional switch architectures no longer meet this need as they cannot accommodate next generation 400 Gbps data rates.
The telecommunication industry is also migrating towards ‘flexgrid’ architectures where the capacity of each channel is moderated to satisfy fluctuating demands. Spare capacity freed up by this can accommodate additional or rerouted traffic flexibly and dynamically by matching channel bandwidths to each signal’s required data rate. This advance relies heavily on software based approaches and these have the added benefit of future proofing networks as the software defined network (SDN) can be remotely modified to accommodate changing demand and new service types, protocols or standards. This is all accomplished without hardware network upgrades or physical interventions, thus reducing costs. The market is expanding with new customers (such as Google and Amazon) joining the existing set of Telco’s and carriers.
Flex-grid networking places severe demands on the underlying hardware, especially optical switches within the network known as a Reconfigurable Optical Add/Drop Multiplexers (“ROADMs”) which must be competitive and have good manufacturability whilst being able to accommodate the flexibility and programmable functionality required. Within ROADM the Wavelength Selective Switches (WSS) is the key component. The ROADM market has grown from zero to $5bn since 2002. The market has already chosen RoadMap’s core technology, namely Liquid crystal on silicon (“LCoS”) as the way in which WSS’s will be made as it has several major advantages. It allows nearly all parameters to be programmable and upgraded by software-remotely and efficiently.
CCMOSS – Parkwalk closes further funding round
We have recently made an investment in Cambridge CMOS Sensors for the UK Tech Fund V and a Parkwalk Syndicate. This follows predecessor funds investing in 2012 and 2013.
Cambridge CMOS Sensors are a leading manufacturer of sensor solutions for monitoring air quality, with a wide range of miniature, ultra-low power gas sensors based on metal-oxide technology and infrared sensor components.
CMOS MEMS platform technology provides a unique silicon platform for CCMOSS’ Metal Oxide (MOX) gas sensors and enables sensor miniaturisation, significantly lower power consumption and ultra-fast response times.
The Micro-hotplates are suspended in a high reliability membrane and act as heater elements for a metal oxide based sensing material. The material resistance will change due to reactions to selected gases and concentrations at temperatures between 200°C to 400°C. Through enabling very fast cycle times, advanced temperature modulation techniques can be used to ensure maximum sensitivity, stability and gas selectivity and minimise measurement times.
Advanced algorithms support the MOX gas sensors family, for maximum selectivity, drift compensation and for self-calibration, enabling easy and timely integration into a wide range of applications.
CCMOSS
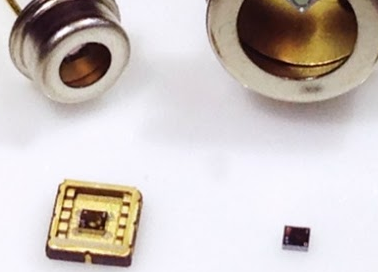
Parkwalk closes investment in Cambridge CMOS Sensors for the UK Tech Fund IV & University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund II.
Cambridge CMOS Sensors is the provider of innovative MEMS high temperature microhotplate technology for gas sensing, flow sensing and lab-on-a-chip applications.
The Cambridge CMOS Sensors technology uses standard CMOS processes that enable high volume, low cost and low power sensor-on-chip solutions.
CCMOSS

Parkwalk closes Cambridge CMOSS investment for the University of Cambridge Enterprise Fund I and the UK Tech Fund III
Cambridge CMOS Sensors is the provider of innovative MEMS high temperature microhotplate technology for gas sensing, flow sensing and lab-on-a-chip applications.
The Cambridge CMOS Sensors technology uses standard CMOS processes that enable high volume, low cost and low power sensor-on-chip solutions.

ARM Holdings – £24.3bn acquisition of the University of Cambridge spin-out
Japan’s Softbank on Monday offered £24.3bn ($32bn) in cash to acquire 100% of ARM Holdings, the UK’s smartphone chip designer that is one of the leaders in the infrastructure of the internet of things.
In 2015, Forbes ranked ARM as the most innovative company in Europe, and the fifth most innovative in the world.
The deal values ARM at 24.4x 2015 revenues or 56.8x 2015 EBITDA.
We believe this is further proof of the value of UK University spin-outs, and their global appeal – ARM have world-wide sales and are unaffected by Brexit as Philip Hammond, the UK’s Chancellor of the Exchequer, said: “Just three weeks after the referendum decision, it shows that Britain has lost none of its allure to international investors.”
“as ARM’s founders will testify, this is the greatest place in the world to start and grow a technology business,” he added.
Softbank’s investment would be the largest ever from Asia into the UK. The deal would “guarantee to double the number of jobs in ARM in the UK over the next five years and turn this great British company into a global phenomenon”.
Over 70bn ARM-designed chips have been shipped to date, with 95% of the world’s smartphones containing at least one ARM-based component, and Canalys estimate 80% of wearable devices sold in 2014 contained at least one ARM-based chip.
Last month Cambridge CMOS Sensors, another spin-out creating next generation internet of things sensors was acquired by ams AG – more detail can be seen here.
Posted on July 18, 2016
Electronics, Fund Managers Comments, Semiconductors
Cambridge, Electronics, Semiconductors